Introduction: Understanding Infinity and Its Use on a Calculator
Infinity is a concept in mathematics that represents a value that is larger than any finite number. While calculators cannot physically display infinity, they can approximate it or represent it using symbols such as INF (infinity), E99, or Overflow.
Whether you’re working with limits in calculus, solving for large numbers, or approximating infinite results, most modern calculators have ways to represent this unbounded concept.
In this article, we will explain:
- How to get infinity on a calculator for limits, large values, and complex equations.
- The use of infinity in different types of mathematical functions.
- Practical examples and step-by-step instructions for scientific calculators, graphing calculators, and basic calculators.
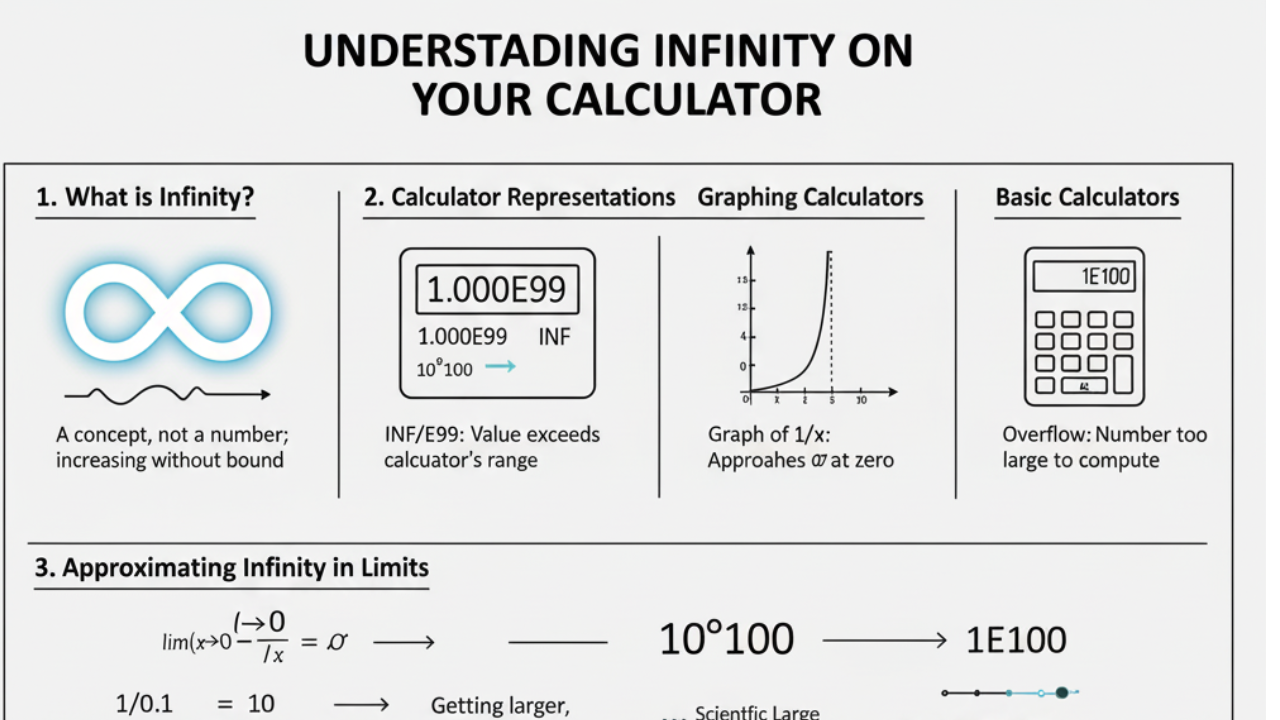
1. What is Infinity?
Infinity is not a number in the traditional sense; it’s a concept. In mathematics, infinity refers to a value that grows without bound. You can think of it as something endless or unlimited. In calculus, infinity is often used to represent values that keep increasing or decreasing indefinitely.
Some common uses of infinity include:
- Limits in calculus: Where functions approach infinity as a value is added or subtracted.
- Scientific notation: Representing extremely large or small numbers.
- Calculations involving very large data sets are especially common in fields like engineering, physics, and finance.
2. How Do Calculators Represent Infinity?
Different types of calculators handle infinity differently. In scientific calculators, large values or undefined results often show as INF, E99, or Overflow, indicating the calculation exceeds the calculator’s capacity.
2.1 Scientific Calculators
Scientific calculators, like those from Casio, TI, or HP, typically handle large numbers by representing them with symbols such as:
- INF: Represents infinity when a number exceeds the calculator’s limit.
- E99: Indicates a number too large to display (e.g., (10^{99})).
- Overflow: This error message is displayed when a calculation goes beyond the allowed value range.
Example:
If you enter (10^{100}) into a scientific calculator, it may display INF or E99, which means the value is too large to be computed or displayed by the calculator.
2.2 Graphing Calculators
Graphing calculators offer more advanced features, allowing you to visualize infinity in functions like exponential growth or logarithmic decay. These calculators show how values approach infinity or negative infinity on a graph, especially for functions like:
f(x) = 1/x (approaches infinity as x approaches 0)
f(x) = e^x (exponentially increases towards infinity)
On a graph, you’ll see vertical asymptotes or functions that grow without bound as they approach infinity.
2.3 Basic Calculators
On basic calculators, representing infinity is more difficult. If the result of a calculation exceeds the calculator’s range, you might see an error message or overflow symbol. However, they can’t handle mathematical operations involving infinity directly (like limits).
3. How to Get Infinity on a Calculator
3.1 Using Limits in Calculus to Approach Infinity
One of the most common ways to use infinity in calculations is through limits in calculus. Calculators cannot directly calculate infinity, but can approximate it by evaluating functions as they approach infinity.
Example: Limit Approach
Consider the following limit:
As x approaches infinity, the value of 1/x approaches zero.
On a calculator, you can approximate this by entering progressively larger numbers for x (e.g., x = 1000, 10000, 100000), and observe how the result gets closer and closer to 0.
Example of Infinity:
To calculate the limit where the result approaches infinity, use:
As x approaches 0, the value of 1/x grows without bound, and on a scientific calculator, you’ll see something like INF (indicating the value is approaching infinity).
3.2 Handling Large Numbers on Scientific Calculators
When working with extremely large numbers, scientific calculators display infinity or E99 as an approximation. For instance:
- Enter ( 10^{100} ) (a number with 100 zeros).
- Your calculator may display INF or E99, indicating that the number exceeds the calculator’s range.
Example of Infinity:
To calculate the limit where the result approaches infinity, use:
As x approaches 0, the value of 1/x grows without bound, and on a scientific calculator, you’ll see something like INF.
3.3 Using Scientific Notation for Large Numbers
Calculators often use scientific notation for extremely large or small values. While this isn’t infinity, it helps approximate large values efficiently. For example, a very large number like ( 10^{100} ) is written in scientific notation as:
1 × 10^100
Scientific calculators will display this as 1E100.
4. Practical Applications of Infinity

4.1 Infinity in Finance
In finance, infinity can represent unlimited growth in compound interest or stock market projections. As time increases, the returns on investments approach infinity, even though actual values may never reach that limit.
4.2 Infinity in Physics and Engineering
In physics, infinity is used to model phenomena such as the speed of light or black holes, where certain values approach infinite limits. Similarly, in engineering, infinity is used in signal processing and control systems.
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Dealing with Infinity on a Calculator
- Confusing large numbers with infinity: Remember, a calculator showing E99 or INF isn’t literally calculating infinity but is indicating that the number is too large to be represented.
- Incorrect limit calculation: When working with limits, ensure you understand that calculators cannot directly calculate infinity but only approximate it.
- Misinterpreting overflow errors: An overflow error means the result of the calculation exceeds the calculator’s range, not that the result is infinite.
6. Conclusion: Mastering Infinity on Your Calculator
While calculators cannot directly display infinity, they are powerful tools for approximating infinite results, especially in limits, scientific notation, and when working with large numbers. Whether you’re dealing with calculus, finance, or physics, knowing how to use your calculator to handle infinite values is essential for efficient problem-solving.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: How do I represent infinity on a calculator?
A1: On scientific calculators, infinity is often represented by INF, E99, or Overflow, indicating that the number is too large for the calculator to process.
Q2: Can I calculate limits involving infinity on a calculator?
A2: While you can’t directly calculate infinity, you can approximate it by inputting increasingly large or small values and observing the results.
Q3: What does INF mean on my calculator?
A3: INF stands for infinity and is displayed when the calculator’s value exceeds its range, such as when you input extremely large numbers or solve for limits approaching infinity.
Q4: How is infinity used in finance?
A4: In finance, infinity represents the unlimited growth of investments over time, such as compound interest, where the value continues growing exponentially.